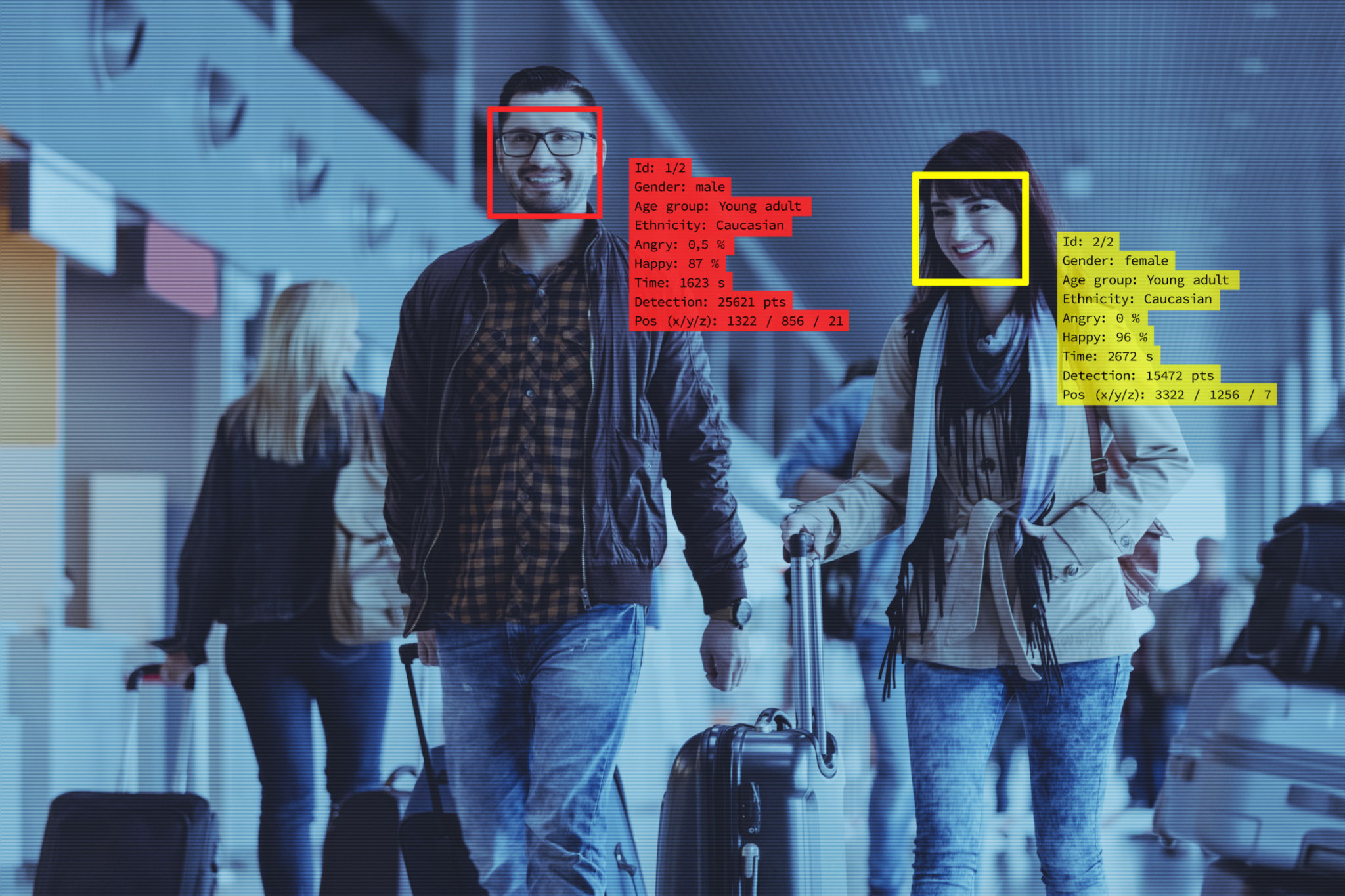
Digital ID and Facial Recognition: Balancing Convenience and Security Against Crime
Introduction
As the digital age advances, innovative technologies like digital ID and facial recognition are revolutionizing identity verification processes. These technologies promise enhanced security and seamless user experiences, but they also introduce new challenges and vulnerabilities. This article explores the intersection of digital ID and facial recognition with criminal behavior, highlighting both the positive impacts and potential risks, including cyber attacks and the threat of hackers stealing sensitive data.

The Promise of Digital ID and Facial Recognition (THE SALES PITCH)
Digital ID and facial recognition technologies offer numerous advantages in today's interconnected world. Digital IDs streamline identity verification, making it easier for individuals to access services and conduct transactions online. Facial recognition adds a layer of security by using unique biometric data to authenticate identities, reducing the risk of identity theft and fraud. Together, these technologies can enhance security in various sectors, including banking, healthcare, and law enforcement, while providing users with convenience and efficiency.
Enhancing Security and Efficiency
One of the most significant benefits of integrating digital ID with facial recognition is the potential to enhance security and efficiency. In financial institutions, for example, facial recognition can expedite the authentication process, allowing customers to access their accounts swiftly and securely. This technology can also be used to prevent unauthorized access, reducing the risk of fraudulent activities. In law enforcement, facial recognition can help identify criminals and solve cases more efficiently, contributing to public safety.

The Dark Side: Cyber Attacks and Data Theft
Despite the promising benefits, integrating digital ID and facial recognition presents SIGNIFICANT risks. Cybercriminals constantly seek to exploit vulnerabilities in these technologies, leading to potential cyber-attacks and data theft. Hackers who gain access to digital ID databases or intercept facial recognition data can steal sensitive personal information, leading to identity theft, financial fraud, and possibly irreparable damage. The centralized storage of biometric data poses a significant risk, as a single breach could compromise the identities of millions of individuals across multiple countries.

Privacy Concerns and Surveillance
The widespread use of facial recognition technology raises concerns about privacy and surveillance. Critics argue that the pervasive deployment of facial recognition systems can lead to UNWARRANTED surveillance, infringing on individuals' privacy rights. There is also the risk of misuse and abuse by GOVERNMENTS or malicious actors, who could use the technology to monitor and control populations. Balancing the benefits of facial recognition with the need to protect individual privacy is a complex challenge that requires careful consideration and regulation.
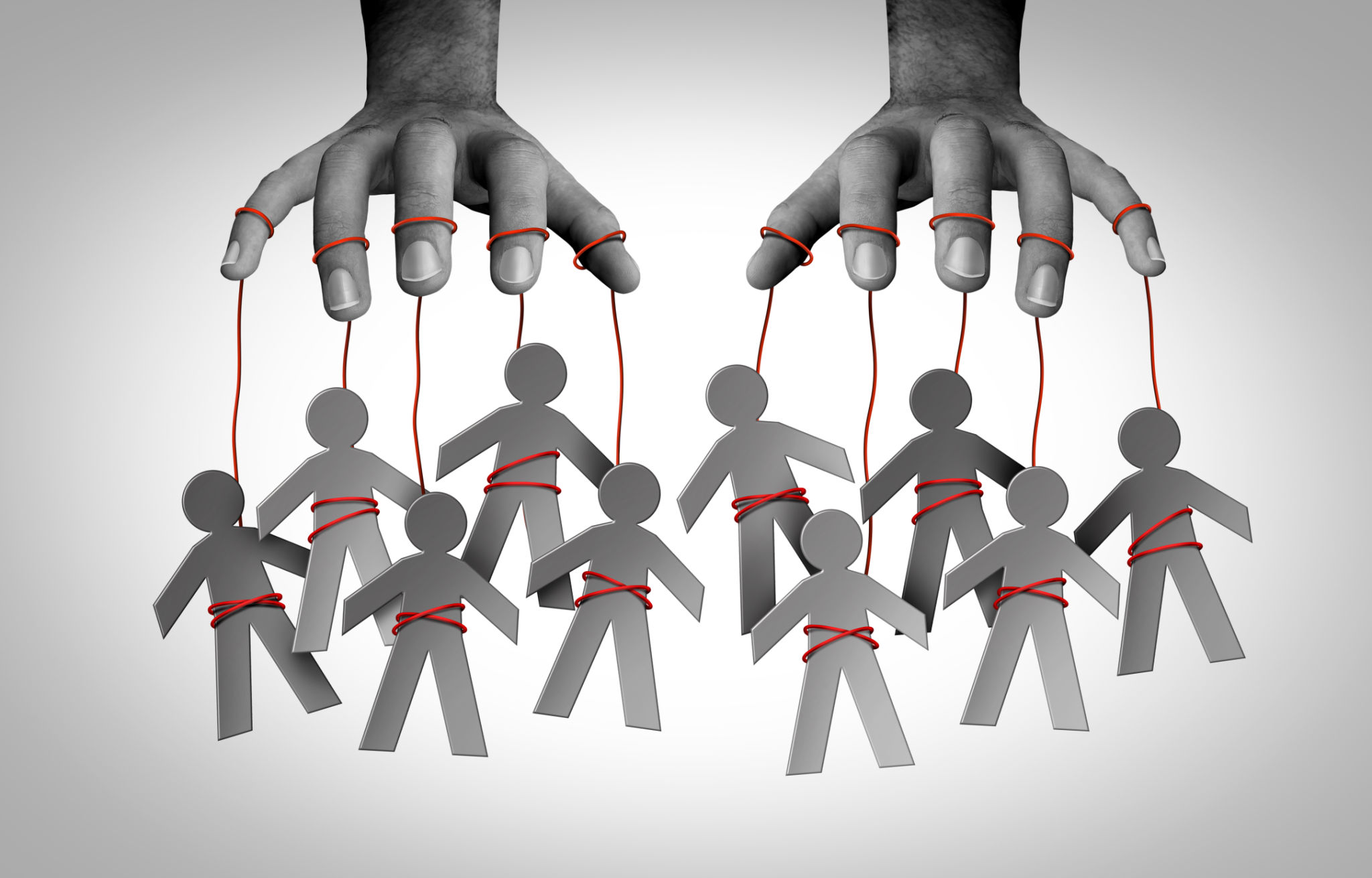

Mitigating Risks: Robust Security Measures
To mitigate the risks associated with digital ID and facial recognition, robust security measures must be implemented. Encryption protocols should be strengthened to protect biometric data during storage and transmission. Multi-factor authentication can add an extra layer of security, reducing the reliance on a single form of identification. Additionally, organizations should adopt DECENTRALIZED storage solutions to minimize the impact of potential data breaches.
Regulatory Frameworks and Standards
Establishing comprehensive and fair regulatory frameworks and industry standards is crucial in addressing the challenges posed by digital ID and facial recognition technologies. Governments and regulatory bodies must enforce stringent data protection regulations to ensure the security and privacy of biometric data while ot abusing their powers. Compliance with standards such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union can help safeguard personal information and hold organizations accountable for data breaches.

Conclusion
Integrating digital ID and facial recognition technologies presents a double-edged sword; on the one hand, it offers enhanced security and convenience, while on the other hand, it poses significant risks to the end user and society as a whole. We live in an age where we continue to walk a fine line between convenience (THE SALES PITCH) and loss of control over our day-to-day lives. As these technologies continue to evolve, it is imperative to strike a balance between leveraging their benefits and mitigating their potential downsides. Understanding the why and WHO is driving the narrative remains critical. Are digital IDs for your safety and convenience, or are they for the safety of those WHO are imposing them? In a world where digital innovation is rapidly transforming our lives, ensuring the people have a choice over what they share and what technology they opt in or out of will no doubt shape the AGENDA leading up to 2030.

